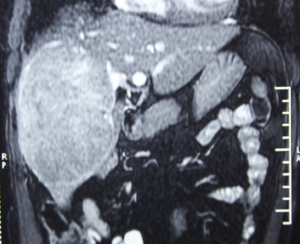
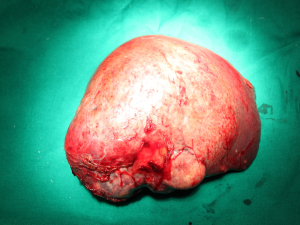
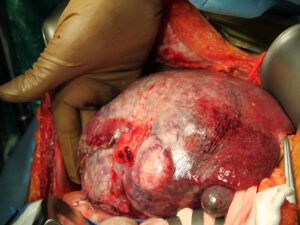
LIVER CANCER
Liver cancer is the uncontrolled growth and spread of unhealthy cells in the liver. Cancer that starts in the liver is primary liver cancer. Cancer that spreads to the liver from another organ (such as bowel or breast) is known as secondary or metastatic liver cancer.
What is the difference between liver tumor and liver cancer ?
Any nodule in the liver is known as a liver tumor. Liver tumors can be non-cancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant). The most common type of cancer that originates in the liver is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
What are the causes of primary liver cancer ?
Some risk factors for liver cancer include:
- Viral hepatitis – Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections . It is estimated that about 5-10 percent of people with HBV or HCV will develop liver cancer.
- Cirrhosis is the end result of all forms of long standing liver damage 5-10 percent of patients with cirrhosis will develop liver cancer.
- Toxins such as Arsenic – Drinking water (usually well water) contaminated with arsenic
- Obesity
- Diabetes
What are the symptoms of liver cancer ?
Liver cancer usually has no obvious symptoms, and people at risk should be followed regularly to detect cancer at an early stage. The following symptoms might be caused by liver cancer:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Anorexia (persistent lack of appetite)
- Early satiety (feeling very full after a small meal)
- Persistent abdominal pain
- Sudden deterioration in the overall condition of a patient with cirrhosis
- Liver enlargement or a mass that can be felt in the area of the liver
What tests will I have to detect liver cancer ?
If liver cancer is suspected, the doctor may order tests such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) blood test, ultrasound scan, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), angiography, laparoscopy and biopsy. It is important to detect liver cancers early because small cancers in a patient who has minimal symptoms can be treated effectively.
What is liver cancer screening ?
Liver cancer screening is the best way to detect liver cancer early in its course. It is performed to detect small cancers that do not produce any symptoms. Patients who have a liver disease that puts them at a high risk of developing liver cancer (such as hepatitis B, any form of cirrhosis) should undergo periodic screening tests.It usually involves a blood test to look for a cancer marker (alpha-feto-protein) and an ultrasound scan of the liver to look for actual cancer. Screening tests are not 100 percent accurate .Your doctor may advise you additional tests if he/she suspects that you may have a liver cancer.
How is liver cancer treated ?
Liver cancer treatment depends on the liver’s condition, size, location, and number of tumors and the person’s age and overall health.
Different ways of treating liver cancer are:
Surgery: If the cancer has been found early and the rest of the liver is healthy, doctors may perform surgery to remove the tumor from the liver.
Cryosurgery: Cryosurgery uses a metal probe to freeze and destroy cancer cells.
Radiofrequency Ablation: Radiofrequency ablation uses a special probe to destroy cancer cells with heat using special needle. The procedure is performed under ultrasound or laparoscopic guidance.
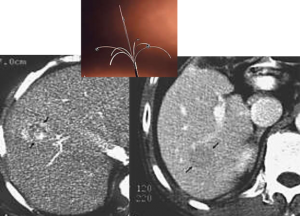
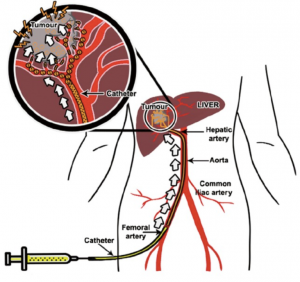
Chemotherapy or chemoembolization: Chemotherapy uses anti-cancer drugs to destroy cancer cells. In some cases, the chemotherapy can be
directly injected into the liver tumor.
Radiation Therapy
Oral chemotherapy drugs : Sorafenib is an oral medication for use in advanced cases of liver cancer.
Can a liver transplant be done for liver cancer ?
Surgery is the most effective therapy for most types of liver cancer, but doctors will usually combine different methods to treat the cancer most effectively. When surgery to remove the cancer itself cannot be performed, your doctor may suggest a liver transplantation.
If I have been diagnosed to have liver cancer, what questions should I ask my doctor ?
You and your family should have a clear understanding of the disease and the treatment plan.
What is my diagnosis?
What is the stage of the disease?
What are my treatment choices? Which do you recommend for me? Why?
What are the chances that the treatment will be successful?
What are the risks and possible side effects of each treatment?
How long will my treatment last?
Will I have to change my normal activities?
What is the treatment likely to cost?
What are the prospects for liver transplantation?